| List of Symbols, Definitions and Units |
|---|
| Macroscopic Variables |
Equation Number |
|
| Other Variables and Constants |
Equation Number |
|
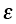 |
Normal (tensile or compressive strain) |
17.7 |
|
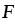 |
Force per unit length on a dislocation (N/m) |
2.4 |
|
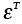 |
Transient strain |
17.9 |
|
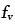 , ,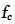 |
Fraction of atom sites associated with lattice and core diffusion respectively |
2.20 |
|
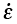 |
Strain rate (s-1) |
1.5 |
|
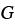 , ,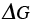 |
Gibbs free energy (J/mol) |
2.6, 2.10 |
|
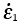 , ,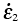 , ,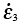 |
Principal strain rates (s-1) |
1.3 |
|
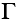 |
Grain boundary energy (J/m2) |
— |
|
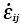 |
Strain rate tensor (s-1) |
1.4 |
|
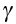 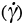 |
Shear strain (rate); see Macroscopic variables |
— |
|
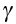 |
Shear strain |
1.3 |
|
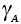 |
Activity coefficient of component A, etc. |
2.28 |
|
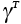 |
Transient shear strain |
17.10 |
|
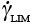 |
Upper limiting strain rate (taken as 106/s) |
17.13 |
|
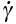 |
Shear strain rate (s-1) |
1.3, 1.4, 1.5 |
|
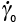 , ,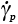 , ,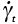 |
Pre-exponential constants (s-1) |
2.9, 2.12, 2.15 |
|
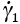 , ,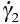 . . . . . .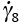 |
Shear strain rates of individual mechanisms (s-1) |
2.1, 2.9, 2.12, 2.21, 2.23, 2.26, 2.29 |
|
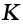 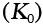 |
Bulk modulus (at 300 K and atmospheric pressure) (MN/m2) |
17.37 |
|
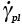 |
Shear strain rate caused by low-temperature plastic mechanisms (s-1) |
3.1 |
|
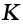 |
Work-hardening constant in tension (MN/m2) |
17.6 |
|
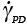 |
Shear strain rate limited by phonon drag (s-1) |
2.14 |
|
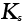 |
Work-hardening constant in shear (MN/m2) |
17.6 |
|
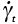 |
Shear strain rate limited by twinning (s-1) |
2.15 |
|
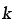 |
Boltzmann's constant (1.381 x 10-23 J/K) |
— |
|
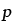 |
Hydrostatic pressure (MN/m2) |
17.37 |
|
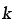 |
Thermal conductivity (J/s m K) |
17.20 |
|
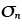 |
Normal (tensile or compressive) stress (MN/m2) |
2.17 |
|
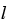 |
Obstacle spacing (m) |
Table 2.1 |
|
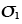 , ,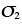 , ,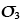 |
Principal stresses (MN/m2) |
1.1 |
|
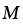 |
Dislocation mobility (m2/Ns) |
2.4 |
|
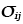 |
Stress tensor (MN/m2) |
1.2 |
|
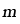 |
Strain hardening exponent |
17.6 |
|
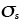 |
Shear stress (MN/m2) |
1.5 |
|
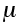 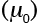 |
Shear modulus (at 300 K and atmospheric pressure) (MN/m2) |
2.1, 2.3, Table 2.1 |
|
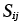 |
Deviatoric part of the stress tensor (MN/m2) |
1.2 |
|
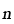 , ,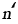 |
Creep exponent |
2.18, 2.19, 2.26 |
|
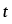 |
Time (s) |
17.3 |
|
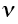 |
Debye frequency (taken as 1012/s) |
2.5 |
|
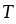 |
Temperature (K) |
1.6, 1.12 |
|
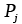 |
Material property |
1.6 |
|
| Other Variables and Constants |
Equation Number |
|
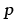 |
Hydrostatic pressure; see Macroscopic variables (MN/m2) |
17.37 |
|
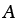 , ,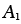 , ,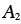 |
Power-law creep constants |
2.18, 2.19 |
|
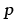 |
Dimensionless exponent |
2.7 |
|
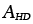 |
Constant for Harper-Dorn creep |
2.23 |
|
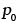 |
Atmospheric pressure (0.1 MN/m2) |
17.37 |
|
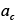 |
Diffusive section of a dislocation core (m2) |
2.20 |
|
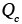 , ,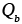 , ,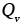 |
Activation energies for lattice, boundary and core diffusion respectively (kJ/mol) |
2.17, 2.20, 2.30 |
|
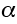 |
Dimensionless ideal strength |
2.1 |
|
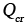 |
Activation energy for creep when different from Qv, Qb or Qc (kJ/mol) |
2.24 |
|
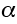 |
Dimensionless constant for low-temperature plasticity |
2.7 |
|
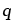 |
Dimensionless exponent |
2.17 |
|
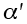 |
Constant for power-law breakdown (MN/m2) |
2.26 |
|
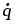 |
Heat generation rate (J/m3 s) |
17.14 |
|
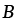 |
Drag coefficient (Ns/m2) |
2.13 |
|
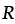 |
Gas constant (8.314 J/mol K) |
— |
|
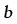 |
Magnitude of Burgers' Vector (m) |
2.2 |
|
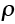 |
Dislocation density (m-2) |
— |
|
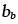 |
Burgers' Vector of boundary dislocation (m) |
17.25 |
|
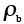 |
Density of boundary dislocations (m-1) |
17.29 |
|
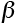 |
Constant for low-temperature plasticity |
2.7 |
|
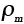 |
Mobile dislocation density (m-2) |
2.3 |
|
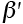 |
Constant for power-law breakdown |
2.26 |
|
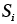 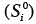 |
State variable (constant initial value) |
1.6, 1.10 |
|
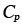 |
Specific heat at constant pressure (J/m K) |
17.16 |
|
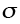 |
Stress; see Macroscopic variables (MN/m2) |
— |
|
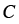 |
Constant for drag-limited glide |
17.12 |
|
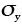 |
Tensile yield strength (MN/m2) |
— |
|
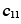 , ,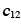 , ,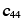 , etc. , etc. |
Single-crystal moduli (MN/m2) |
— |
|
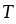 |
Absolute temperature; see Macroscopic variables (K) |
1.6, 1.12 |
|
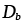 |
Boundary diffusion coefficient (m2/s):
Db=D0bexp-(Qb/RT) |
2.30 |
|
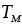 |
Melting temperature (K) |
— |
|
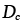 |
Core diffusion coefficient (m2/s):
Dc=D0cexp-(Qc/RT) |
2.20 |
|
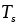 |
Temperature of surroundings (K) |
17.20 |
|
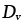 |
Lattice diffusion coefficient (m2/s):
Dv=D0vexp-(Qv/RT) |
2.17 |
|
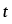 |
Time; see Macroscopic variables (s) |
— |
|
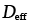 |
Effective diffusion coefficient for power-law creep or diffusional flow (m2/s) |
2.20, 2.30 |
|
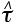 |
Flow strength (in shear) for obstacle cutting at 0 K (MN/m2) |
2.6, 2.7 |
|
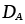 , ,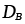 |
Tracer diffusion coefficients for components A and B (m2/s) |
2.27, 2.28 |
|
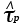 |
Lattice resistance of Peierls stress (in shear) at 0 K (MN/m2) |
2.10, 2.12 |
|
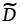 |
Chemical interdiffusion coefficient (m2/s) |
2.28 |
|
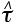 |
Twinning stress at 0 K (MN/m2) |
2.15 |
|
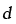 |
Grain size (m) |
2.29, 2.30 |
|
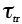 |
Threshold stress for creep (MN/m2) |
17.35 |
|
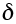 |
Diffusive thickness of a grain boundary (m) |
2.30 |
|
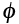 , ,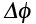 |
Chemical potential (J/atom) |
17.27 |
|
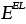 |
Elastic energy of a dislocation (J/m) |
— |
|
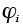 , ,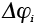 |
Interface potential barrier (J/atom) |
17.24 |
|
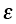 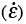 |
Normal strain (rate); see Macroscopic variables |
— |
|
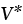 |
Activation volume (m3) |
17.49 |
|
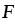 , ,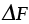 |
Helmholtz free energy (J/mol) |
2.6, 2.7, 2.10 |
|
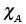 , ,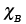 |
Atom fractions of A and B |
2.27, 2.28 |
|
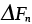 |
Free energy of twin nucleation (J/mol) |
2.15 |
|
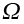 |
Atomic or molecular volume (m3) |
2.17 |
|
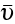 |
Average dislocation velocity (m/s) |
2.3, 2.5 |
|
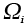 |
Ionic volume (m3) |
2.29 |
|
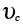 |
Average climb velocity (m/s) |
2.17 |
|
|